The waste and recycling industry is undergoing a major transformation due to the integration of technology, including Artificial Intelligence (“AI”) and robotics. These technologies are revolutionising the way waste is managed, sorted and recycled.
According to the UN Environment Programme’s report “Global Waste Management Outlook 2024”, the amount of waste we generate globally is predicted to grow from 2.1bn tonnes in 2023 to 3.8bn tonnes by 2050. Even so, the picture is looking promising in the UK. While total waste production is expected to grow by 15% by 2050, increased recycling and incineration is reducing the amount going to landfill.
In 2022, approximately 13.1m metric tons of municipal waste was sent to landfills in the UK; nearly half of the volume recorded in 2010. Much of this reduction is attributed to the landfill tax which made it more expensive to dispose of waste in this way. This has led to a boost in recycling rates, although this dipped during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Also, incineration with energy recovery accounted for nearly half of local authority collected waste disposal in England in 2022. However, this process is criticised for its low energy yield and high emissions.
New waste legislation took effect in England in March 2025 requiring workplaces to separate dry recyclable materials (plastic, metal, glass, paper, and card), food waste, and residual (non-recyclable) waste.
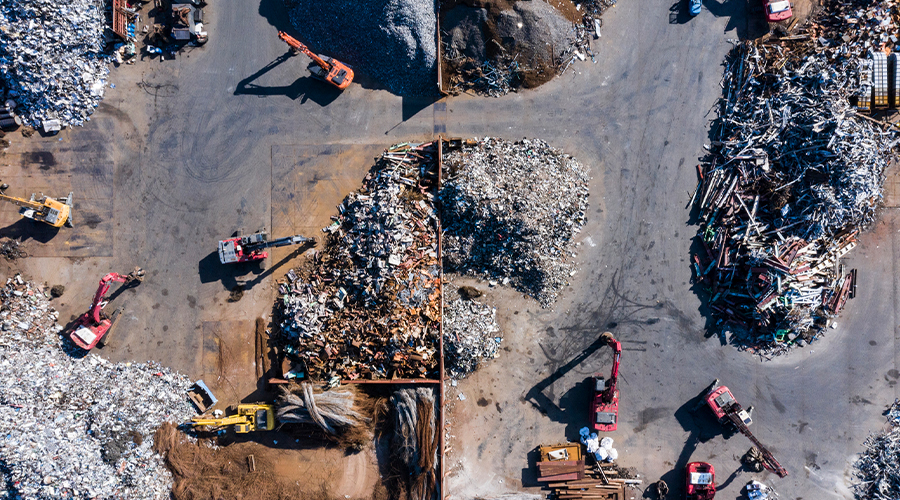
Technology, too, is helping the waste and recycling industry. Traditional waste sorting methods are often reliant on manual labour with people spotting and picking out recyclables. This is time-consuming, costly and prone to errors. Manual waste sorting can also be hazardous, exposing workers to harmful substances and physical injuries.
AI for improvements in accuracy and speed
Barcelona uses smart waste bins with weight sensors and volume tracking to optimise collection routes and schedules.
AI-powered systems, coupled with robotics, offer significant improvements in sorting accuracy and speed. These solutions already exist, with hundreds of thousands of installations across more than 100 countries including in Singapore, Seoul and San Fransisco, from suppliers such as ZenRobotics, AMP and Tomra. The solutions use cameras and optical sensors with machine learning algorithms and pattern recognition to differentiate between various types of plastics, metals and paper.
Future systems will likely use spectroscopy – the study of colour – and chemical analysis to identify materials with even greater precision. Robotic arms with grippers will then handle the different waste types. These AI and robotic systems can sort materials far quicker and more accurately than humans, reducing time, contamination rates of recycling and injuries to workers.
Another notable advantage of AI and robotics in waste management is the optimisation of waste collection routes. AI systems can analyse data from smart bins equipped with sensors to monitor waste levels in real-time. This information can be used to optimise collection schedules and routes, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. This process will minimise the number of trips required for waste collection based on predicted volumes, or maximise the efficiency of the route to help lower fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
What next?
The population continues to grow and so does the volume of waste it produces. Operators in the waste sector are likely to continue to embrace technology and should consider the following:
- Increased adoption of smart bins to optimise collection
- With the changes requiring workplaces to sort their recyclable materials, this might lead to the use of compartmentalised vehicles to handle separated waste, or separate or more frequent collections to handle the recyclables
- Adoption of AI and robotics at the waste facility to sort recyclables and non-recyclables
- Sale of sorted recyclables to generate a new revenue stream.